Be sure to know the signs and symptoms of a blood clot and what your risk factors may be.
Blood clots are usually helpful. They form whenever we cut or scrape our skin to stop the bleeding and prevent infection. However, when blood clots form where they shouldn’t or don’t dissolve like they should, they can be dangerous and cause serious health problems.
Learn more about blood clots and your risk of developing one, as well as what symptoms to look out for.
What Is a Blood Clot?
A blood clot is a mass of blood that forms when platelets, proteins and cells in the blood stick together. Most blood clots are harmless, like the ones that form after you get hurt, but blood clots that don’t dissolve or that form where they shouldn’t can be dangerous.
The dangerous effects of a blood clot depend on its location within your body:
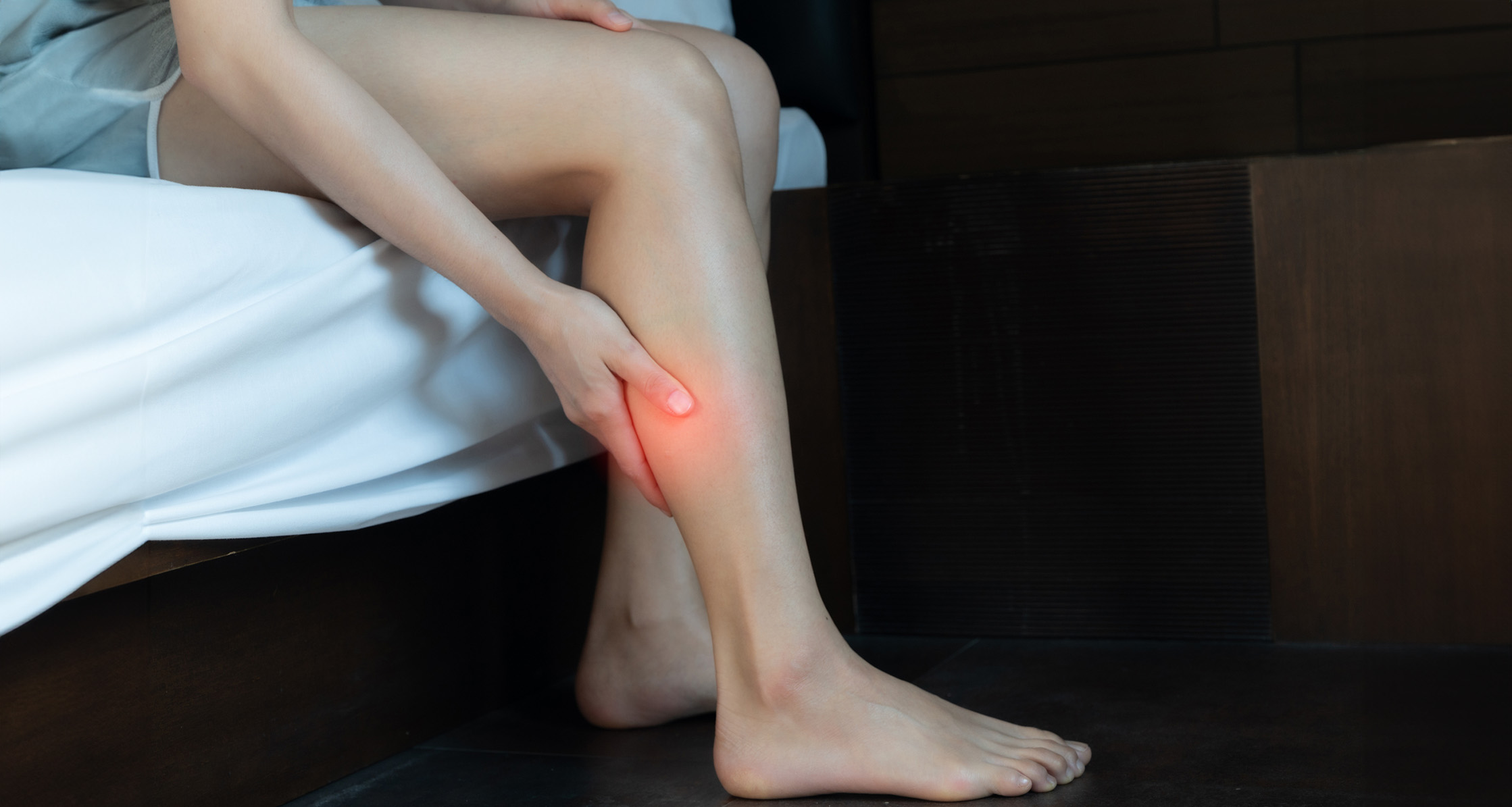
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) – DVT usually forms in a person’s legs or sometimes in their arms. DVT can partly or completely block blood flow through a vein, causing damage to the limbs.
- Pulmonary embolism (PE) – If DVT is not treated, a clot can move into a person’s lungs and become a PE. This calls for immediate medical attention and can be fatal.
What Are the Signs of a Blood Clot?
According to the National Blood Clot Alliance, on average, one person dies of a blood clot every six minutes. That’s why it’s important to learn how to recognize the signs of a blood clot.
The signs of a blood clot can vary greatly, depending on where it is in your body. For example, a blood clot blocking blood flow to the lungs or the heart can cause symptoms like shortness of breath or chest pain. A blood clot within your leg may cause swelling, pain or discolored skin.
Signs of DVT may include:
- Swelling, usually in one arm or leg
- Leg pain or tenderness, often described like a charley horse
- Reddish or blueish skin discoloration
- Warmth in the arm or leg
If you have symptoms of DVT, talk to your health care provider right away.
Signs related to a PE may include:
- Sudden shortness of breath
- Chest pain that’s sharp and stabbing
- Rapid heart rate
- Unexplained cough, sometimes with bloody mucus
A PE can be fatal. If you experience any symptoms of a PE, call an ambulance or 911 right away.
Am I At Risk of a Blood Clot?
Anyone can develop a blood clot, but there are certain factors that make it more likely for one to develop – including your family history, lifestyle choices and certain diseases or disorders can increase risks of developing a blood clot.
Here are some risk factors to consider:
- Injury to a vein often caused by a fracture, severe muscle injury or surgery
- Limited movement or confinement to a bed due to an injury, surgery or illness
- Pregnancy and giving birth
- Estrogen-containing contraceptives and hormone replacement therapy
- Heart disease
- Lung disease
- Cancer and its treatments
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- An inherited clotting disorder
- Family history of blood clots or a previous blood clot of your own
- Obesity
- Age (risk increases as age increases)
- A catheter located in a central vein
What Steps Can I Take to Prevent a Blood Clot? 
You may be able to decrease your risk or prevent blood clots by taking the following steps:
- Be active. Move around as soon as possible after being confined to bed, like after a surgery, illness or injury.
- Get up and move every few hours. After long car rides, a flight or sitting for a long time, move around. Even sitting you can raise and lower your heels or tighten and release your muscles to keep blood flowing.
- Know your risk factors. Talk to your health care provider about your risk factors for blood clots. For example, if you have a family history of blood clots, your provider may put you on a blood thinner.
- Get regular physical activity. Blood clots are more likely when you have a sedentary lifestyle. Be sure you are moving and keeping your body healthy.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Obesity can cause several health conditions that may contribute to an increased risk of blood clots.
- Don’t smoke. Lung disease can increase your risk for blood clots.
- Talk to your health care team. If you are hospitalized for any reason, talk to your health care team about strategies to prevent the risk of blood clots, such as getting out of bed regularly, taking medications and more.
Where Can I Find More Information about Blood Clots?
- The National Institutes of Health offers more details about how a blood clot forms, including a video animation.
- The CDC has a helpful infographic that explains more about the symptoms and risk factors associated with blood clots. They also cover specific blood clot risks associated with cancer, travel and pregnancy.
Be sure to know the signs and symptoms of a blood clot and what your risk factors may be. Talk to your health care provider to ensure you’re doing what you can to avoid a dangerous blood clot.